Laibin Huang, Ph.D.
Assistant Professor
Biology
Courses Taught
BIOL 4640 - General Microbiology; BIOL 4160 - Microbial Ecology
Education
Ph.D., University of Florida
Research Interests
I am a microbiologist, and my studies have focused on “Microbial Ecology” using the combination of classical techniques (qPCR, amplicon sequence, isotopes), state-of-the-art omics (metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, and metabolomics) and bioinformatic tools (high-performance computing, python, snakemake, R program).
With the vast functional and metabolic diversity, microorganisms are integral to all the earth’s ecosystems; however, they change constantly throughout the time and space. Meanwhile, the intensive human activities and global climate changes pose great challenges to and complications for the understanding of their dynamics and the quantification of their roles in contributing to ecosystem functions and health. Hence, my research has aimed to explore the roles that microorganisms play in adapting to and mitigation of global changes.
My research lies at the intersection of Microbial Ecology, Bioinformatics, and Soil
Science, with an overarching goal to understand how microorganisms drive and sustain
ecosystem functions. My work focuses on two interconnected themes: (1) Community ecology of soil microbiome—exploring how microbial communities assemble and adapt to environmental disturbances;
(Fig.1A and 1B); and (2) Microbial controls on Nitrogen (N) cycling—uncovering how soil microbiome regulates N transformation and contributes to soil
fertility and health (Fig.1C).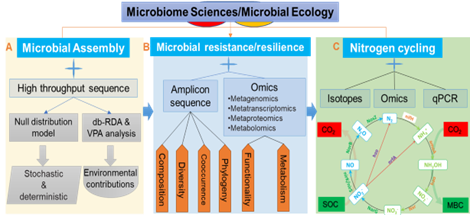
Figure 1: Overview of research focus
- Community Ecology of Soil Microbiomes
The central questions driving this research are: (a) how microbes with different functional traits assemble in diverse ecosystems; and (b) how these assembly processes affect their environmental resistance and resilience. My studies reveal that microbial communities demonstrate varying degrees of recovery and adaptation in terms of their composition, physiology, and functions, resulting in unevenly recovery processes in response to environmental shifts. The representative studies include:
- Huang, L. et al. (2024). Microbiota recovery in a chronosquences of impoverished Cerrado soils with biosolids applications. Sci Total Environ, 931, 172958.
- Huang, L. et al. (2022). Different stochastic processes regulate bacterial and fungal community assembly in estuarine wetland soils. Soil Biol Biochem, 167: 108586.
- Zhang, G.,..Huang, L., et al. (2022). Plant invasion reconstructs soil microbial assembly and functionality in coastal salt marshes. Molecular Ecology, 31(17), 4478-4494.
- Huang, L. et al. (2021). Desalinization via freshwater restoration highly improved microbial diversity, co-occurrence patterns and functions in coastal wetland soils. Sci Total Environ, 765: 142769.
- Huang, L. et al. (2020). Microbial resistance and resilience in response to environmental changes under the higher intensity of human activities than global average level. Glob Change Biol, 26: 2377-2389. [Highlighted in Ecology, Environment & Conservation, 1020, ISSN: 1945-6506]
Collectively, these works establish that microbial assembly and adaptation are ecosystem specific and process dependent, providing a framework for predicting microbiome resilience across diverse classes of environmental changes.
- Microbial Controls on Nitrogen Cycling
My second research focus examines microbial controlling N cycling that is central to soil fertility and health. My studies demonstrate that agricultural management led to distinct diversification of N regulating microorganisms with different nutrient acquisition strategies and gene expression patterns. The representative studies include:
- Li, H…. Huang, L et al. (2025) Decadal climate warming drives divergent responses in soil nitrifying populations. (under review)
- Brandão Gontijo, J., Huang, L., et al. (2025). Depth-dependent Metagenome-assembled Genomes of agricultural Soils under Managed aquifer Recharge. Scientific data, 12(1), 858.
- Huang, L., et al. (2023). Molecular and Dual-Isotopic Profiling of the Microbial Controls on Nitrogen Leaching in Agricultural Soils under Managed Aquifer Recharge. Environ Sci Technol, 57(30), 11084-11095.
- Zhao, J., Huang, L., et al (2023). Nitrogen and phosphorous acquisition strategies drive coexistence patterns among archaeal lineages in soil. ISME J, 17(11), 1839-1850.
- Huang, L., et al. (2021). Ammonia-oxidizing archaea are integral to nitrogen cycling in a highly fertile agricultural soil. ISME Commu, 1(1), 1-12. [The best of ISME Communications in 2021]
- Huang, L., et al. (2021). Campylobacterota dominate the microbial communities in a tropical karst subterranean estuary, with implications for cycling and export of nitrogen to coastal waters. Environ Microbiol, 23(11), 6749–6763. [Highlighted in New of Science, 1222, ISSN:1944-2564,]
- Huang, L., et al. (2019) Long-term N fertilization imbalances potential N acquisition and transformations by soil microbes. Sci Total Environ, 691, 562-571.
Altogether, this body of work provides mechanistic insights into how functional diversity and evolutionary adaptation among N-cycling microbes shape N transformation, regulate nutrient use efficiency and sustain ecosystem resilience.
Labs and Facilities
Huang lab website (https://seahuanglaibin.wixsite.com/sluhuang)
Publications and Media Placements
Recent publications (5 years):
Google Scholar page or CV for a full publication list:
Brandão, G.J., Huang, L., Levintal, E., Prieto G.C., Erikson, C.B., **Coyotl, A., ... & Mazza Rodrigues, J.
L. (2025). Depth-dependent Metagenome-assembled Genomes of agricultural Soils under
Managed aquifer Recharge. Scientific data, 12(1), 858.
*Klein, M. L., Erikson, C. B., McCabe, C. J., Huang, L., Rodrigues, J. L., & Mitloehner, F. M. (2025). Limited Effects of Tannin Supplementation
on the Dairy Cattle Fecal Microbiome with Modulation of Metabolites. Frontiers in
Microbiology, 16, 1570127.
**Nguyen, T. T., Altman, A., Huang, L., Rodrigues, J. L. M., Dahlke, H. E., Kamennaya, N. A., & Levintal, E. (2025). A portable
low‐cost incubation chamber for real‐time characterization of soil respiration. Soil
Science Society of America Journal, 89(1), e20800.
Huang, L., Soares, R.A., Wright, A., Corrêa, R.S., Silva, L., Rodrigues, J.L.M. (2024). Microbiota
recovery in a chronosquences of impoverished Cerrado soils with biosolids applications.
Science of The Total Environment, 931, 172958.
Silva, D. F., Rodrigues, J. L. M., Erikson, C., Silva, A. M., Huang, L., Araujo, V. L., ... & Cardoso, E. J. (2024). Grazing exclusion-induced changes in
soil fungal communities in a highly desertified Brazilian dryland. Microbiological
Research, 285, 127763.
*Silva, DF., Cardoso, E., Huang, L., Erikson, C., Silva, A., Araujo, V., Silva, D., Melo, V., Ferreira, A., Pereira,
A., Rodrigues J. (2024). Functional genes related to N and P cycling in degraded and
restored areas from Brazilian drylands. Applied Soil Ecology 196, 105316.
Huang, L., Levintal Elad, Christian B. Erikson. Coyotl Adolfo, Dahlke Helen E., Horwath William
R, Rodrigues Jorge L. Mazza. 2023. Molecular and dual-isotopic profiling of the microbial
controls on nitrogen leaching in agricultural soils under managed aquifer recharge.
Environmental Science & Technology. 2023, 57, 30, 11084–11095
Zhao J., Huang L., Chakrabarti S., Cooper J., Choi E., Ganan C., Tochinsky B., Triplett E., Daroub
S.H., Martens-Habbena W. 2023. Nutrient acquisition strategies drive coexistence patterns
among globally predominant archaeal lineages in soil. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1839-1850.
Levintal, E., Huang, L., García, C. P., Coyotl, A., Fidelibus, M. W., ... Rodrigues, J. L. & Dahlke, H. E.,
2023. Nitrogen Fate During Agricultural Managed Aquifer Recharge: Linking Plant Response,
Hydrologic, and Geochemical Processes. Science of the Total Environment, 864:161206
Huang, L., Bai, J., Wang J., Zhang G., Wang W., Wang X., Zhang L., Wang Y., Liu X., and Cui
B. 2022. Different stochastic processes regulate bacterial and fungal community assembly
in estuarine wetland soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 167: 108586.
Zhang, G., Bai, J., Tebbe, C.C., Huang, L., Jia, J., Wang, W., Wang, X., Yu, L. and Zhao, Q., 2022. Plant invasion reconstructs
soil microbial assembly and functionality in coastal salt marshes. Molecular Ecology, 31:4478–4494.
Yu, L., Bai, J., Huang, L., Zhang, G., Wang, W., Wang, X., and Yu, Z. 2022. Carbon-rich substrates altered
microbial communities with indication of carbon metabolism functional shifting in
a degraded salt marsh of the Yellow River Delta, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 331, 129898.
Zhang, G., Bai, J., Tebbe, C.C., Huang, L., Jia, J., Wang, W., Wang, X., Zhao, Q., Wen, L., Kong, F. and Xi, M., 2022. Habitat-specific
responses of soil organic matter decomposition to Spartina alterniflora invasion along
China's coast. Ecological Applications, e2741.
Huang, L., Chakrabarti, S., Cooper, J., Perez, A., John, S., Daroub, S., and Martens-Habbena,
W. 2021. Ammonia-oxidizing archaea are integral to nitrogen cycling in a highly fertile
agricultural soil. ISME Communications, 1(1), 1-12.
Huang, L., Bea, H., Young, C., Pain, A., Martin, J.B., and Ogram, A. 2021. Campylobacterota
dominate the microbial communities in a tropical karst subterranean estuary, with
implications for cycling and export of nitrogen to coastal waters. Environmental Microbiology, 23(11), 6749–6763.
Huang, L., Zhang G., Bai J., Xia Z., Wang W., Jia J., Wang X., Liu X., and Cui B. 2021. Desalinization
via freshwater restoration highly improved microbial diversity, co-occurrence patterns
and functions in coastal wetland soils. Science of the Total Environment, 765: 142769.
Yu, M., Su, W., Huang, L., Parikh, S.J., Tang, C., Dahlgren, R.A., and Xu, J. 2021. Bacterial community structure
and putative nitrogen-cycling functional traits along a charosphere gradient under
waterlogged conditions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 162, 108420.
Wang, L., Chen, H., Wu, J., Huang, L., Brookesa, P., Rodriguesc, J., Xu, J., and Liu, X. 2021. Effects of magnetic biochar-microbe
composite on Cd remediation and microbial responses in paddy soil. Journal of hazardous materials, 44: 125494.
Zhang, G.L., Bai, J., Tebbe, C.C., Huang, L., Jia, J., Wang, W., Wang, X., Yu, L., and Zhao, Q. 2020. Spartina alterniflora invasions
reduce soil fungal diversity and simplify co-occurrence networks in a salt marsh ecosystem.
Science of The Total Environment, 143667.
Huang, L., Bai, J., Wen, X., Zhang, G., Zhang, C., Cui, B. and Liu, X. 2020. Microbial resistance
and resilience in response to environmental changes under the higher intensity of
human activities than global average level. Global Change Biology, 26: 2377-2389.
Behnke, G. D., Zabaloy, M. C., Riggins, C. W., Rodríguez-Zas, S., Huang, L., and Villamil, M. B. 2020. Acidification in corn monocultures favor fungi, ammonia
oxidizing bacteria, and nirK-denitrifier groups. Science of The Total Environment, 720(10):137514.
Huang, L., Riggins C. W., Rodríguez-Zas S., Zabaloy M. C., and Villamil M. B. 2019. Long-term
N fertilization imbalances potential N acquisition and transformations by soil microbes.
Science of the Total Environment, 691: 562-571.
Pain, A., Martin, J.B., Young, C.R., Huang, L., and Valle-Levison, A. 2019. Organic carbon quantity and quality across salinity
gradients in conduit-versus diffuse flow-dominated subterranean estuaries. Limnology & Oceanography, 64(3): 1368-1402.
Bae, H., Huang, L., White, J., Wang, J., Delaune, R., and Ogram, A. 2018. Response of microbial populations
regulating nutrient biogeochemical cycles to oiling of coastal saltmarshes from the
Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environmental pollution, 241, 136-147.